Have you ever wondered about the age of Mount Shasta? It's a question that has intrigued many, and in this article, we will explore the fascinating journey of determining the age of this majestic mountain. From geological evidence to scientific studies, we will uncover the clues that have helped researchers estimate the age of Mount Shasta. Get ready to embark on a journey through time as we unveil the mysteries behind this iconic natural wonder.
Age of Mount Shasta
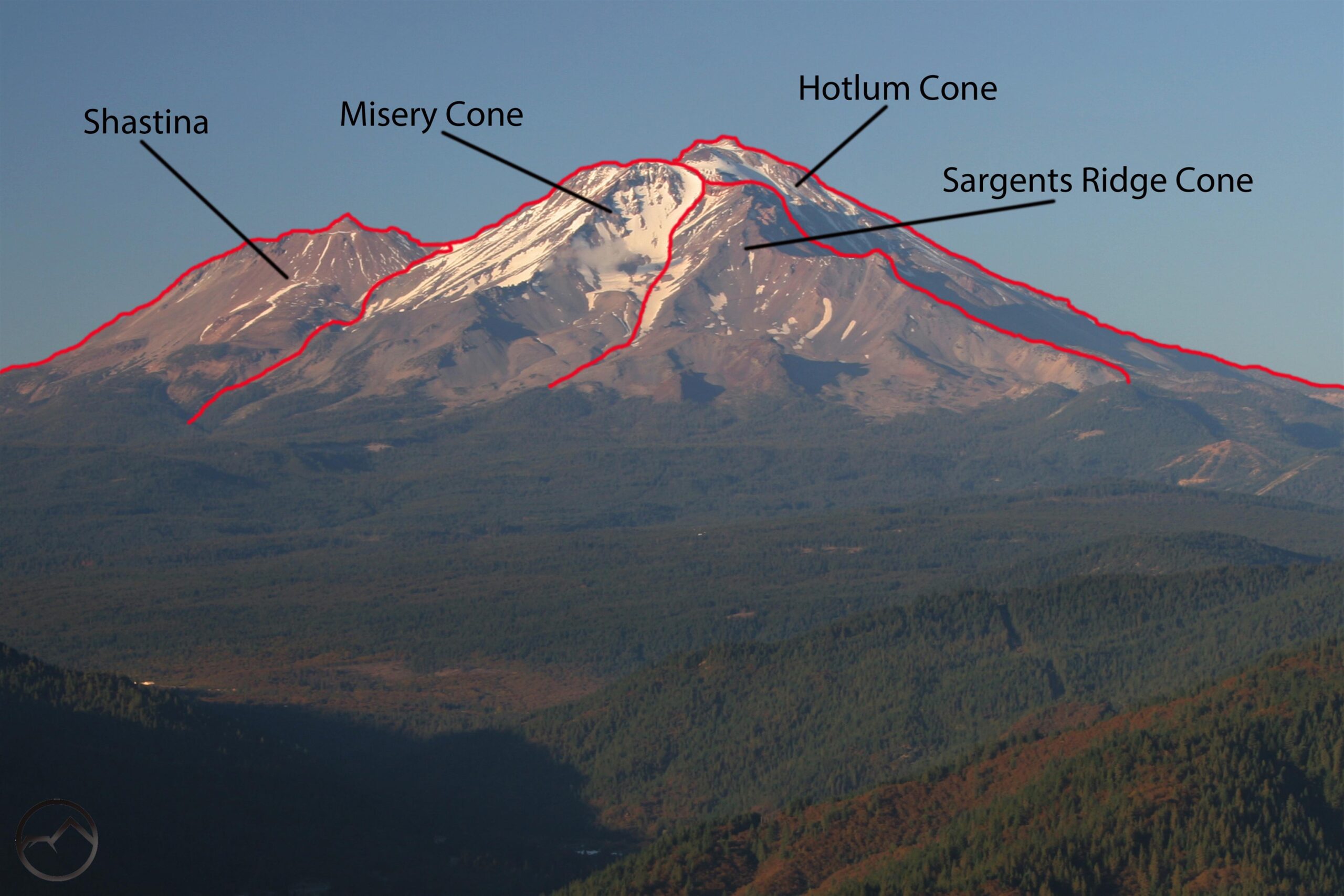
Mount Shasta, located in northern California, is a majestic and iconic volcanic peak that has captivated people for centuries. In order to truly appreciate the history and significance of this natural wonder, it is important to understand its age and the processes that have shaped its formation. Through the study of volcanic history, geological formation, and radiometric dating, scientists have been able to unravel the mysteries of Mount Shasta's ancient origins.
Volcanic History
The volcanic history of Mount Shasta spans millions of years. It is part of the Cascade Range, a line of volcanic peaks that stretches from northern California to British Columbia. The period of volcanic activity in this region began around 600,000 years ago and is still ongoing today. Mount Shasta is considered one of the most active volcanoes in the United States, with its last eruption occurring in 1786.
Geological Formation
Mount Shasta is an impressive stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, which is formed by layers of lava, ash, and other volcanic materials. The geological formation of Mount Shasta is closely linked to the Pacific Plate, one of the major tectonic plates that make up the Earth's crust. It is situated at the southern end of the Cascadia subduction zone, where the Pacific Plate is slowly diving beneath the North American Plate.
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating is a method used by scientists to determine the age of rocks and minerals based on the decay of radioactive isotopes. Through the analysis of different isotopes present in volcanic rocks from Mount Shasta, researchers have been able to estimate the age of the volcano. This dating technique has provided valuable insights into the timeline of Mount Shasta's formation and activity.
Volcanic History of Mount Shasta
Period of Volcanic Activity
The period of volcanic activity in the Mount Shasta region started approximately 600,000 years ago during the Pleistocene epoch. Over this extended period, numerous eruptions and lava flows have occurred, shaping the landscape and adding to the height of the volcano. These eruptions have been both explosive and effusive, with varying levels of intensity and magma compositions.
Eruptions and Lava Flows
Throughout its history, Mount Shasta has experienced both explosive eruptions and more tranquil lava flows. Explosive eruptions occur when highly viscous and gas-rich magma is trapped beneath the surface, leading to the buildup of pressure and eventual release through explosive volcanic activity. Lava flows, on the other hand, are a result of less viscous magma reaching the surface and flowing down the slopes of the volcano.
Geological Formation of Mount Shasta
Location and Structure
Mount Shasta is situated in Siskiyou County, California, near the border with Oregon. With an elevation of over 14,000 feet, it stands as one of the tallest peaks in the Cascade Range. The mountain itself is composed of various layers of volcanic rocks, including andesite, dacite, and basalt. Its symmetrical cone shape and prominent snow-capped peak make it an iconic landmark in the area.
Plate Tectonics and Volcanism
The geological formation of Mount Shasta is closely tied to the movements of tectonic plates. It is located near the point where the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath the North American Plate. As the subducting plate sinks into the mantle, it melts, forming magma chambers that eventually feed volcanic eruptions. The convergence of these plates creates the ideal conditions for the formation of composite volcanoes like Mount Shasta.
Radiometric Dating of Mount Shasta
Methodology
Radiometric dating involves the analysis of radioactive isotopes present in volcanic rocks to determine their age. One commonly used method to date rocks is the potassium-argon dating technique. This method relies on the decay of potassium-40 to argon-40, with a known half-life of approximately 1.3 billion years. By measuring the ratio of parent isotope (potassium-40) to daughter isotope (argon-40) in a sample, scientists can calculate the age of the rock.
Results and Implications
Through radiometric dating of volcanic rocks from Mount Shasta, scientists have determined that the oldest rocks in the area date back to around 600,000 years ago. These rocks correspond to the earliest eruptions that formed the foundation of the volcano. Subsequent eruptions and lava flows over thousands of years have added to the sheer size and complexity of Mount Shasta.
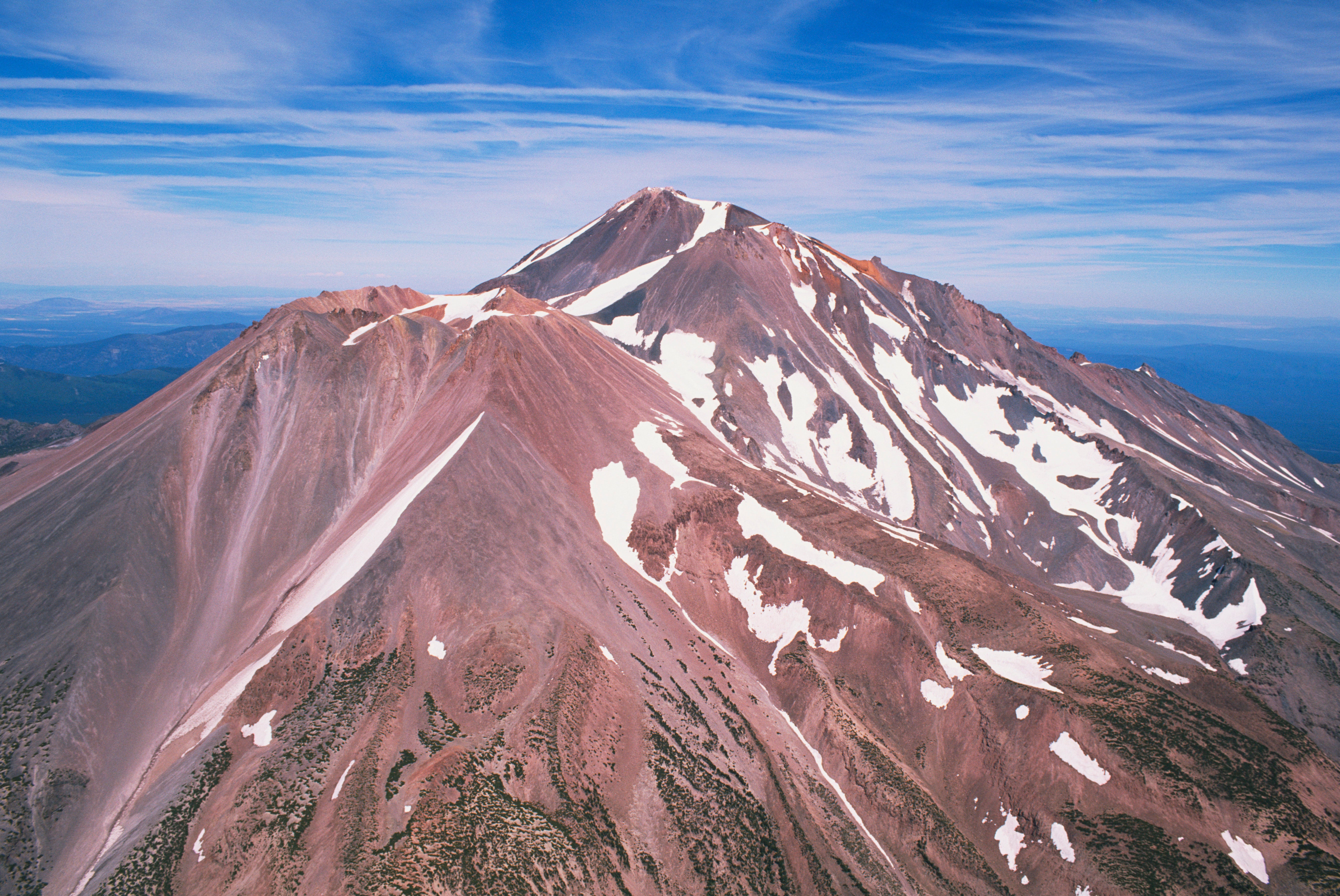

The Formation and History of Mount Shasta
Pre-Mount Shasta Era
Before Mount Shasta came into existence, the region was part of the Klamath Mountains, which formed through intense tectonic activity during the Jurassic era. Sediment deposition over millions of years created the foundation on which Mount Shasta would eventually be built. These ancient geological processes set the stage for the birth of this magnificent volcanic peak.
Building of the Volcano
The building of Mount Shasta began with the formation of a basement complex and early volcanism during the Pleistocene epoch. As magma rose to the surface, it interacted with the existing rocks, creating new layers and adding to the height of the volcano. Over time, the repeated eruptions and lava flows shaped the landscape, forming Shasta Valley and the surrounding areas.
Glacial Activity and Shasta Bally Period
During the last ice age, glacial activity played a significant role in shaping Mount Shasta and its surroundings. Glaciers formed on the upper slopes of the volcano, carving out valleys and leaving behind moraines and U-shaped valleys. As the climate warmed and glaciers retreated, a period known as the Shasta Bally was experienced. Volcanic domes and lava flows emerged during this time, further adding to the complexity of Mount Shasta.
Significance of Radiometric Dating
Radioactive Isotopes and Decay
Radiometric dating relies on the principle of radioactive decay. Some isotopes found in rocks are unstable and gradually decay over time, transforming into a more stable isotope. By measuring the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes, scientists can determine the amount of time that has elapsed since the rock formed or last underwent a significant change. This technique has revolutionized our understanding of geological processes and the age of Earth's features.
Reliability of Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating is a highly reliable method for determining the age of rocks and minerals. It is based on well-established principles of physics and has been extensively tested and validated. While some factors, such as contamination or loss of parent or daughter isotopes, can potentially impact the accuracy of dating, scientists have developed rigorous protocols to minimize these sources of error.
Dating Techniques Used for Mount Shasta
In the case of Mount Shasta, radiometric dating techniques such as potassium-argon dating have been employed to determine the age of volcanic rocks. Analysis of these rocks has yielded valuable information about the timeline of the volcano's formation and the duration of its eruptive history. These findings have contributed to a deeper understanding of Mount Shasta's significance and geological evolution.

Conclusion
Understanding the age and formation of Mount Shasta provides a fascinating glimpse into Earth's geological history and the forces that have shaped our planet. Through the study of volcanic history, geological formation, and radiometric dating, scientists have pieced together a comprehensive picture of Mount Shasta's past. Furthermore, this research opens up avenues for future studies and exploration of the volcano's ongoing geological processes. By appreciating Mount Shasta's geological significance, we can better appreciate the immense beauty and natural wonders that our world has to offer.